
Are you tired of dealing with the pesky bumps on your face that just won’t go away? Are you wondering whether these bumps are dangerous or if there’s a way to treat them?
Welcome to the world of sebaceous hyperplasia! This blog post will delve into this common and benign skin condition, guiding you through its causes, identification, and treatment options. Say goodbye to the uncertainty and hello to a clear understanding of sebaceous hyperplasia.
Understanding Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Sebaceous gland hyperplasia, also known as benign sebaceous hyperplasia or senile sebaceous hyperplasia, is a skin condition where the sebaceous glands enlarge, resulting in painless bumps on the face and upper trunk.
As stated. sebaceous hyperplasia occurs when the sebaceous glands, which are responsible for producing oil to lubricate the skin, undergo an abnormal growth and enlargement. This condition is often seen in older individuals, hence the term “senile” sebaceous hyperplasia.
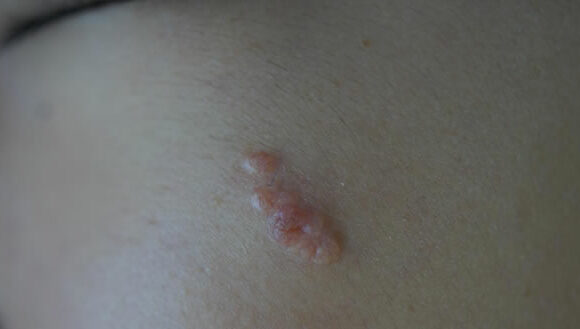
These bumps are typically skin-colored or yellowish, with a central pit and visible blood vessels. While this condition is harmless and does not have malignant potential, it can be a nuisance for those who develop it.
Let’s dive deeper into the role of sebaceous glands and how to identify sebaceous hyperplasia.
The Role of Sebaceous Glands
Sebaceous glands serve a crucial role in maintaining skin health by producing an oily substance called sebum. This oily substance protects the skin from external elements, keeping it moisturized and healthy.
If you have oily skin, hormones can significantly impact your skin’s oil production capacity. Furthermore, testosterone has the strongest effect, as it prompts the sebaceous glands to produce more sebum.
During puberty, this increased oil production can lead to the enlargement and heightened activity of sebaceous glands, with the peak occurring during the third decade of life.
One might wonder if hormones play a similar role during pregnancy. Interestingly, transplacental maternal androgens have a significant effect on fetal sebaceous glands, resulting in heightened activity and the production of a protective layer called vernix caseosa.
However, these hormonal fluctuations can also contribute to the development of sebaceous hyperplasia in susceptible individuals.
Identifying Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Sebaceous hyperplasia is distinguished by bumps that are the same color as the skin or have a yellowish hue. The bumps should have a distinct dimpled center and exhibit visible blood vessels.
These bumps differ from acne, which is caused by a blockage of hair follicles leading to an accumulation of oil and dead skin cells beneath the skin.
There are rare variants of sebaceous hyperplasia, such as:
- linear sebaceous hyperplasia
- zosteriform
- diffuse
- giant
- nevoid
- familial forms, including functional familial sebaceous hyperplasia
Nevoid sebaceous hyperplasia, mistaken for other skin conditions, can be a concern due to its appearance, but it is also a benign condition and one of the more common benign skin tumors.
Regardless of the variant, it’s essential to accurately identify sebaceous hyperplasia to choose the most suitable treatment.
Factors Contributing to Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Several factors can contribute to the development of premature sebaceous gland hyperplasia, including age-related hormonal changes, genetic predisposition, and certain medications or medical conditions. Let’s explore each of these factors in more detail to better understand their role in causing sebaceous hyperplasia.
Age and Hormonal Changes
Aging and hormonal fluctuations can contribute to the development of sebaceous hyperplasia, particularly in middle-aged and older individuals. As age advances, androgen levels tend to decrease, resulting in a decrease in sebaceous gland activity and oil production. This underlying hormonal shift can lead to the overproduction of sebum, causing sebaceous hyperplasia.
It is important to note that hormonal changes are the primary factor responsible for sebaceous hyperplasia. Thus, understanding and managing these changes can play a crucial role in preventing and treating this condition.
Genetic Predisposition
Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to sebaceous hyperplasia, increasing their risk of developing the condition.
A mutation in the gene controlling sebum production can lead to this genetic predisposition.
Muir-Torre syndrome is one rare genetic condition that can cause sebaceous hyperplasia. It is a serious and, unfortunately, incurable condition. This autosomal dominant disorder increases the risk of developing sebaceous gland carcinoma.
Understanding one’s genetic risk factors can help in the early detection and management of sebaceous hyperplasia. If you have a family history of this condition, it’s essential to monitor your skin and consult a dermatologist if you notice any changes.
Medications and Medical Conditions
Certain medications, such as immunosuppressants, and medical conditions, like HIV, can increase the likelihood of sebaceous hyperplasia. Medications like cyclosporine are also associated with sebaceous hyperplasia.[1] These medications may affect sebum production, leading to the development of sebaceous hyperplasia bumps.
It’s crucial to be aware of the potential side effects of medications and the impact of medical conditions on your skin.
If you suspect that a medication or medical condition is contributing to sebaceous hyperplasia, consult with your healthcare provider to discuss alternative treatments or management strategies.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
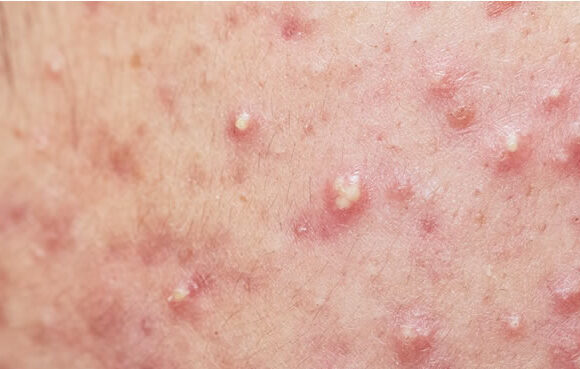
Diagnosing intraoral sebaceous hyperplasia typically involves visual examination and dermoscopy, with biopsy and lab studies used to rule out other conditions, such as basal cell carcinoma.
Let’s explore these diagnostic methods in more detail and understand how they help in accurately diagnosing sebaceous hyperplasia.
Visual Examination and Dermoscopy
Visual examination and dermoscopy are essential tools in identifying sebaceous hyperplasia and differentiating it from other skin conditions.
The visual examination involves inspecting the skin using the naked eye or lighted instruments, while dermoscopy is a non-invasive diagnostic technique that uses a handheld device with a magnifying lens and a light source to examine the skin in detail.
Through visual examination and dermoscopy, healthcare professionals can observe the characteristic yellowish-white papules with a central depression, which are indicative of sebaceous hyperplasia.
Other skin conditions may have distinguishing features that can be identified through these diagnostic methods, helping to rule out more severe or malignant conditions.
Biopsy and Lab Studies
In some cases, a biopsy and lab studies may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis of sebaceous hyperplasia and rule out more serious conditions, such as skin cancer.
A biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small sample of tissue is extracted from the body for further examination under a microscope to ascertain the presence of any disease or abnormality.
Histopathological examination of sebaceous hyperplasia lesions reveals enlarged glands with normal morphology, each containing mature sebaceous lobules that connect to a dilated principal sebaceous duct.
Blood tests, imaging tests, and genetic testing may also be necessary to eliminate the possibility of more serious conditions, such as skin cancer.
Treatment Options for Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Although there is no known cure for sebaceous hyperplasia, various treatment options are available to manage the condition and improve the appearance of the skin. These options include treatment for sebaceous hyperplasia, such as:
- Topical medications
- Oral medications
- In-office procedures
- Alternative treatments
Let’s explore these systemic treatment options in more detail.
Topical and Oral Medications
Topical and oral medications can help manage sebaceous hyperplasia but may require ongoing use to maintain results. Topical treatments include retinoids, antibiotics, and topical steroids, while oral medications include isotretinoin and oral antibiotics. [2]
These medications work by reducing the size of sebaceous glands, decreasing oil production, and addressing any underlying bacterial infection that may be present.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any topical or oral medications for sebaceous hyperplasia.
They can help determine the most appropriate treatment based on your specific needs and monitor your progress throughout the treatment process.
In-Office Procedures
In-office procedures, like laser therapy and cryotherapy, can effectively treat sebaceous hyperplasia but may carry risks of scarring or discoloration.
Laser therapy, such as the use of Argon and carbon dioxide (CO2) lasers, has been demonstrated to reduce the thickness of the lesions and result in smoother skin with minimal scarring.
Cryotherapy involves the use of freezing temperatures to eliminate sebaceous hyperplasia bumps, causing them to dry up and drop away.
Another in-office procedure is electrocautery, which involves using an electrical charge to burn the bumps. This procedure can cause changes in the color of the skin in the affected area. If it is not performed accurately, it can lead to indentation scars.
It’s crucial to consult with a dermatologist to determine the most appropriate in-office procedure for your individual case.
Alternative Treatments and Sebaceous Hyperplasia Treatment at Home
Alternative treatments for sebaceous hyperplasia include herbal remedies, home remedies, and dietary modifications.
Some natural remedies involve lemon juice, apple cider vinegar, peppermint oil, mint juice, turmeric powder, red clover extract, and witch hazel.
Products containing retinol or salicylic acid can also be used to treat lesions, potentially reducing the size of the glands and unclogging pores.
Another alternative treatment option is photodynamic therapy, which involves the following steps:
- Application of a drug to the affected cells, rendering them sensitive to light
- Subsequent controlled exposure of the cells to intense light
- Destruction of the affected cells
While these alternative treatments may help manage sebaceous hyperplasia, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment approach for your specific needs.
Tips for Preventing Sebaceous Hyperplasia

Preventing sebaceous hyperplasia involves maintaining a proper skincare routine and protecting the skin from sun damage. By adopting a consistent skincare regimen and using sun protection, you can reduce your risk of developing this benign skin condition.
Let’s take a closer look at these preventative measures.
Skincare Routine
A consistent skincare routine, including gentle cleansing and moisturizing, can help reduce the risk of sebaceous hyperplasia. Here are some tips to follow:
- Use a cleanser containing salicylic acid or low levels of retinol to effectively unclog pores and reduce oil production.
- Exfoliate periodically to remove dead skin cells and prevent clogged pores.
- Look for products containing ingredients such as retinol, niacinamide, and salicylic acid, which can help manage oil production and reduce the likelihood of sebaceous hyperplasia.
By incorporating these steps into your skincare routine, you can help maintain healthy skin and reduce the risk of sebaceous hyperplasia.
It’s essential to tailor your skincare routine to your specific skin type, whether you have darker skin, fair skin, or anything in between.
Consulting with a dermatologist or skincare professional can help you determine the most appropriate products and regimen for your unique needs.
Sun Protection
Sun protection, such as using sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, can help prevent sebaceous hyperplasia by minimizing sun damage to the skin.
It’s important to apply sunscreen daily, even on cloudy days, as UV rays can still penetrate through clouds and damage the skin.
In addition to sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses, can further shield your skin from harmful sun exposure.
By taking these preventative measures, you can reduce the risk of developing sebaceous hyperplasia and promote overall skin health.
Summary
In conclusion, sebaceous hyperplasia is a benign skin condition resulting from the enlargement of sebaceous glands.
Although it is harmless, understanding the factors contributing to its development, accurately diagnosing it, and exploring various treatment options can help manage this condition and improve the appearance of the skin.
By maintaining a consistent skincare routine, using sun protection, and seeking professional advice when necessary, you can take control of your skin’s health and prevent sebaceous hyperplasia from impacting your daily life.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you get rid of sebaceous hyperplasia?
For sebaceous hyperplasia, treatments range from Retinol to Surgery, and it is best to follow the most common advice for which one would be most suitable.
In order to get rid of sebaceous hyperplasia, it is important to consult a doctor for the best treatment plan.
Can you squeeze sebaceous hyperplasia?
It is not recommended to squeeze sebaceous hyperplasia bumps. Attempting to do so can cause them to become swollen, red, and inflamed, or even bleed.
It is best to leave them alone and seek medical advice if they become bothersome.
What does sebaceous hyperplasia look like?
Sebaceous hyperplasia is characterized by small whitish-yellow bumps ranging from 1 to 4 mm in diameter. These bumps contain a central pit and, in some cases, may have visible blood vessels around the edge.
In general, they look like tiny lumps surrounded by a white-yellow color.
What is sebaceous hyperplasia?
Sebaceous hyperplasia is a benign skin condition that appears as small, skin-colored, or yellowish bumps on the face, particularly around the nose, cheeks, and forehead.
It typically affects adults of middle age or older and is thought to be caused by an overgrowth of sebaceous glands.
With proper treatment, this condition can be effectively managed.
What causes sebaceous hyperplasia?
Sebaceous hyperplasia is caused by a combination of environmental factors such as aging, genetics, and certain medications or medical conditions.
- [1 | 2] Farci F, Rapini RP. Sebaceous Hyperplasia. [Updated 2022 Sep 5]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562148/
- Farci F, Rapini RP. Sebaceous Hyperplasia. 2022 Sep 5. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan–. PMID: 32965819.
More Content
- What is Fungal Acne
- Top-Rated Benzoyl Peroxide Face Wash for Acne
- The Best Moisturizers for Fungal Acne in 2023
- Fungal Acne Cleansers – An Updated List
- Moisturizer Alternatives to Avene Tolerance Extreme Emulsion
- Forehead Fungal Acne
- 18 SunScreens for Fungal Acne
- Fungal Acne-Safe Toners Your Skin Will Love
- The Importance Of Patch Testing Skincare Products
- Malezia Skincare: A Game-changer for Fungal Acne
